System and Security: Managing MS Windows autostart programs.
When Windows starts up, lots of programs and services are automatically started. Such programs are called autostart programs. It is obvious that a great part of them is mandatory to run in order to have a working Windows system. Another part is required to run given applications correctly. However, there is also a part of these autostart programs, that we don't need, or even that we don't want. For example, if we install several database servers, but normally work with MySQL, it doesn't make any sense to start PostgreSQL at Windows start (instead, start it manually, when you need it). Disabling autostart for programs, that we don't need all the time is good practice for 2 reasons. First, their start slows down the startup of Windows. Second, when running, they unnecessarily use system resources.
Whereas applications like Apache or MySQL ask during installation if you want the service started when Windows starts up, lots of applications configure some of their components to be autostart programs, without informing the user. Sometimes, it's the program itself. In most cases, it's a program that automatically checks for updates. Eventually, it's a program that annoys you with trying to convince you to upgrade from the free version, that you are actually running, to a commercial license. Managing the autostart programs is thus something, that every computer user should regularly do.
The tutorial is based on my experiences on Windows 10. It should apply to Windows 11, too.
Windows autostart programs - A big mess!
Whereas on a Linux operating system, all programs that start up automatically can be found at one location, on MS Windows, there are several possibilities to make a program start when Windows starts up.
- In the Windows file system, there are two folders called StartUp. Placing the shortcut of a program into these
folder, will start the programs when Windows starts up. The paths to these folders are:
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\StartUp, and
C:\Users[User Name]\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup.
This way to automatically start a program is rarely used on modern Windows releases, and if you have a look at their content, you will probably notice that they are empty. - Most autostart programs are configured as such in the Windows Registry. If you read Internet articles about
autostart programs, they mostly tell you that the corresponding registry keys are found in
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run.
This is true, however, there are several other registry folders that are used to configure the automatic start of programs. One example is the folder
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\StartupApproved\Run. - The automatic startup of server programs is configured in Windows Services, where you may disable a service, or set it to be started automatically, or manually.
- Finally, a program can be started automatically via Windows Task Scheduler, by triggering its execution with the option "at login of any user", or "at login of <user-name>".
Autostart programs in Windows Settings.
A simple way to manage (a part) of the autostart programs is to use Windows Settings. From the Start menu, choose Windows Settings > Apps > Startup. This not only lists the autostart programs, but also gives you the possibility to enable/disable the automatic startup of one of these programs using a switch button.
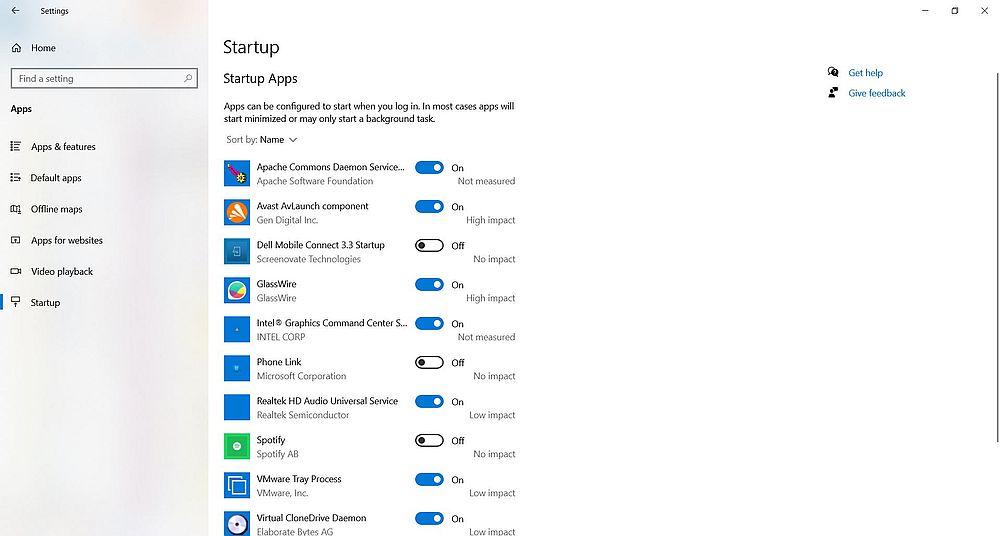 |
Autostart programs in Windows Task Manager.
This is essentially the same as in Windows Settings, but it also allows to display the program’s properties. Right-click the taskbar at the bottom of the screen, and from the opening context-menu, choose Task Manager. In the Task Manager window, open the Startup tab. You can choose which columns are actually displayed by right-clicking one of the column names. This opens a list with the available columns. Check the Command line item, to also display the path to the program.
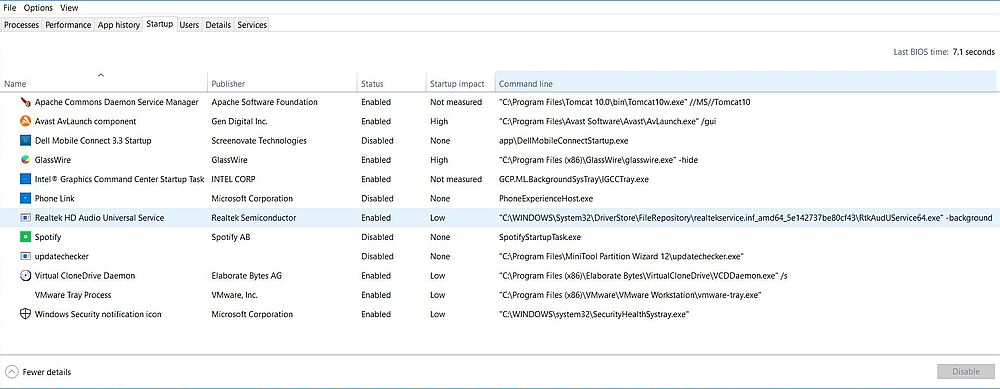 |
Right-clicking one of the items shown, gives you the possibility to enable/disable its automatic startup. You can also open the file location of the executable, or the executable's properties.
Note: For some of my autostart programs (ex: Spotify), the "Open file location" and "Properties" options were dimmed. No idea, what's the reason of that (?).
Autostart programs in the Windows Registry.
To open the Windows Registry Editor, right-click on the Windows icon in the task bar at the bottom of the screen, and choose Run, then in the opening dialog box, type "regedit" (without the quotes). You can browse the registry the same way that you browse the file system. Just double-click a folder icon in the left pane to open it. You can edit the value of a key, or delete a key by choosing the corresponding entry of the right-click context menu. Warning: Do not edit the registry, unless you are absolutely sure what you are doing!
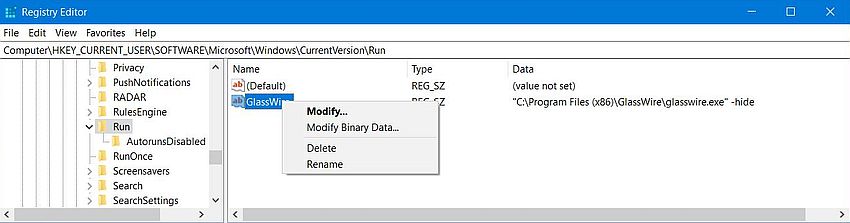 |
Editing autostart keys in the Registry is, for example, useful, if you notice that the path to the executable to be run has been incorrectly set.
Autostart of Windows Services.
Open Windows Administrative Tools > Services from the Start menus. The opening window shows all installed services. You can then start/stop a service, set it to start automatically/manually, as well as enable/disable it. Warning: Do not make any changes to service settings, unless you are absolutely sure what you are doing!
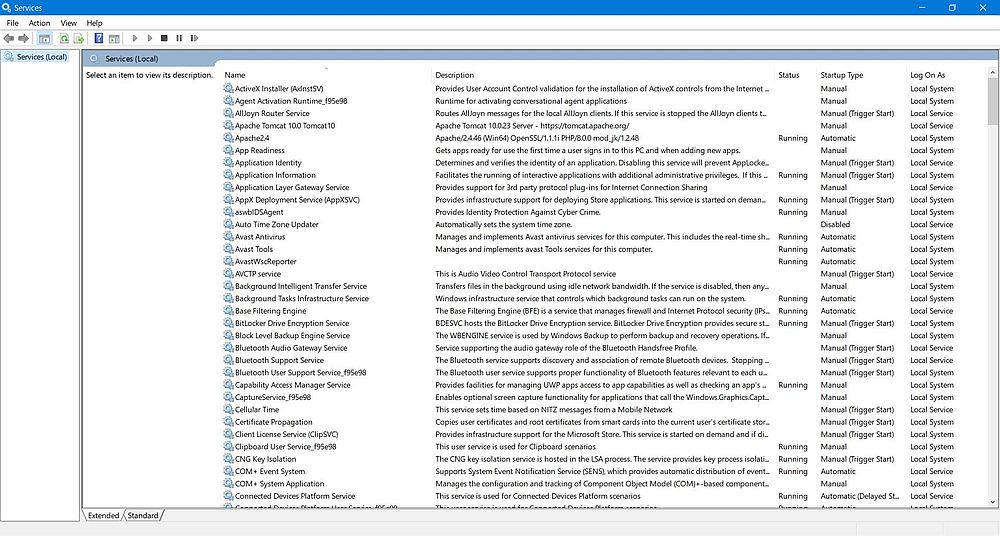 |
Autostart via Windows Task Scheduler.
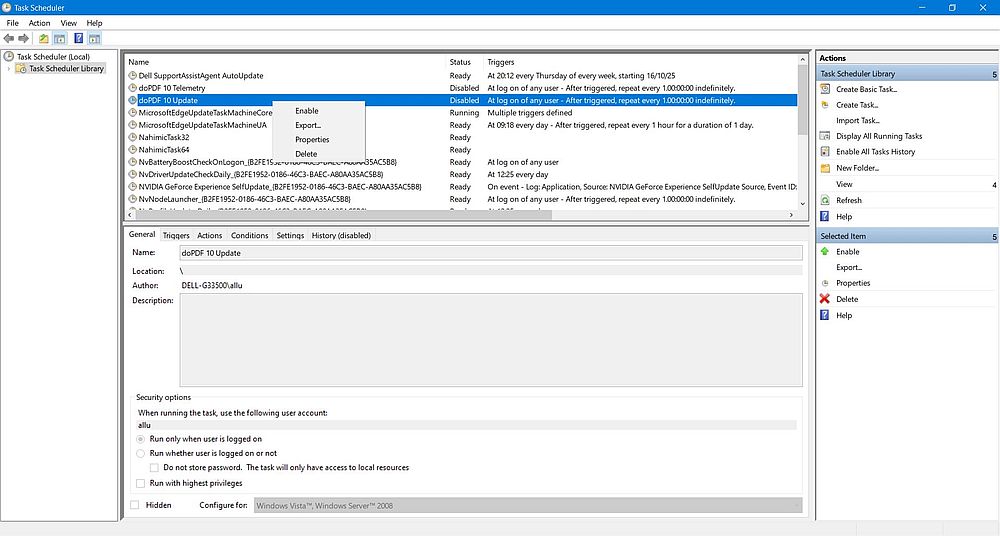
Open Windows Administrative Tools > Task Scheduler from the Start menus. The opening window shows all tasks actually scheduled. Among them, you can find some that configure the automatic start of a program at Windows startup (example on the screenshot: the disabled task "doPDF 10 Update"). You can here view/edit a task's properties, as well as disable it or delete it, i.e. remove the task from Task Scheduler.
 |
Using the freeware application WhatInStartup.
WhatInStartup by Nirsoft is mentioned on several websites as being the ideal tool to manage autostart programs in Windows. Maybe this was the case with earlier versions of Windows (the software is said to work from Windows XP up to Windows 8 on the vendor's website). On my Windows 10, it was not really what I was looking for. First, not all autostart programs listed in Task Manager were listed in WhatInStartup. And (at least it seems so), after having disabled an autostart program, it finishes by no more being displayed in the WhatInStartup.
Using Autoruns from Sysinternals.
The (probably) best choice to mange autostart programs is Autoruns, that is actually part of the Sysinternals tools by Microsoft. You can download the GUI application and the corresponding command line program from learn.microsoft.com. The download is a ZIP archive containing the different files. Store the files into some folder (I use "C:\Programs\Autoruns"). For your own convenience, you may want to create a shortcut of Autoruns.exe on the desktop, or in your Start menu.
To avoid problems, you should run this application as administrator. To do this by default, right-click the shortcut, that you use to launch the application, and choose Properties, push the Advanced button, and select the Run as Administrator checkbox.
Autoruns searches a dozen of places to find autostart programs (you can limit the search, if you want). The result is that you'll get a rather long list of programs, drivers, and DLLs.
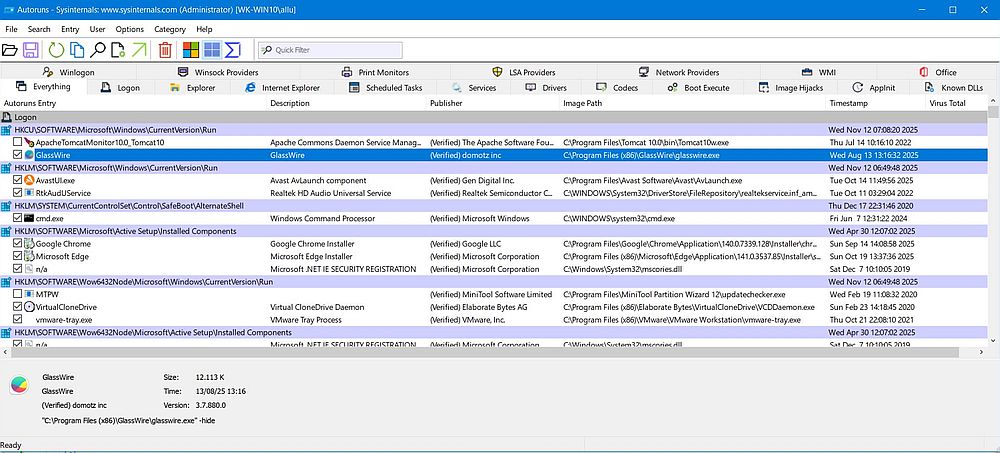 |
The application allows you enable/disable the automatic start of a program when Windows starts up (select resp. unselect the corresponding checkbox), to delete an autostart entry, to view the executable's properties, and (this is nice!) to check the executable using the VirusTotal online application.
Note: Despite all these places where Autoruns is looking at, there are autostart programs, that will not be detected; example on my Windows 10: Spotify.
If you find this text helpful, please, support me and this website by signing my guestbook.